What is the Technical Intern Training Program?
TITP commenced in 1993 in Japan. The program aims to contribute to developing countries by accepting its people and transferring skills through On-the-job Training (OJT) in Japan. It promotes international cooperation through transfer of skills, techniques and knowledge gained by technical interns to the developing nations. This will not only contribute to the human resource development but will drive economic growth of the said regions.
To amplify the impetus on making India the skill capital of the world, the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), Government of India, has initiated several measures. One such noteworthy measure is the signing of the Memorandum of Cooperation (MoC) with the Ministry of Justice, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. The MoC was signed on October 17,
2017 to significantly expand the bilateral cooperation between India and Japan in the skill development sector. Under the program, selected candidates from India undergo three-to-five years of internship in Japan, after which they are required to return to India and utilize the skills acquired by them in Japan. In January 2018, MSDE appointed National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) to monitor the program.
Overview of the new Program under the Technical Intern Training Act
① Establishment of basic principles for technical intern training and responsibilities of and basic policies for involved persons |
② System of accreditation for technical intern training plans |
③ Notification system for implementing organizations |
④ Licensing system for supervising organizations |
⑤ Establishment of Organization for Technical Intern Training as an approval organization (Website of the Organization for Technical Intern Training) (in Japanese only) |
⑥ Establishment of rules on requests for cooperation and so on to ministers with authority over businesses, and creation of regional councils by relevant administrative agencies and other bodies |
① Creation of penalties for violations of human rights and so on |
② Creation of new system for technical intern trainees to submit notices to the competent ministers |
③ Creation of consultation and reporting services for technical intern trainees |
④ Enhanced support for changing training sites |
① Extension of training period for excellent supervising organizations and implementing organizations (from three years to five years) |
② Increased technical intern trainee quotas for excellent supervising organizations and implementing organizations |
③ Expansion of approved occupations (regionally limited occupations, occupations unique to companies, and simultaneous training in multiple occupations) |
1 Overview of the Technical Intern Training Program
The Technical Intern Training Program was established as a formal program in 1993 based on the high evaluations of training programs conducted by overseas local companies and others in the form of employee education starting in the late 1960s.
The objectives and purpose of the Technical Intern Training Program are to transfer skills, technologies, or knowledge (“Skills etc.”) accumulated in Japan to developing and other regions and to promote international cooperation by contributing to the development of human resources who can play roles in the economic development of those developing regions.
The objectives and purpose have remained constant since the establishment of the Technical Intern Training Program in 1993, and the Technical Intern Training Act provides that a fundamental principle of the program is that “technical training shall not be conducted as a means of adjusting labor supply and demand” (Article 3, Paragraph 2 of the Act).
The particulars of the Technical Intern Training Program are intended to form employment relationships between corporations, sole proprietors, and other businesses in Japan with technical intern trainees so that the trainees can acquire, master, or enhance Skills etc. that would be difficult to acquire in their home countries. The training period is a maximum of five years, and acquisition of Skills etc. is conducted pursuant to technical intern training plans.
2 Procedure for Accepting Technical Intern Trainees
There are two types of procedures for accepting technical intern trainees: individual enterprise type and supervising organization type.
As of the end of 2016, 3.6% of acceptances were individual enterprise type and 96.4% were supervising organization type (based on the number of technical intern trainees present in Japan).
- ❶ Individual enterprise type:
A format whereby enterprises and other businesses in Japan (implementing organizations) accept employees of overseas local subsidiaries, joint venture companies, or trading partners for technical intern training - ❷ Supervising organization type:
A format whereby non-profit organizations such as business cooperatives and societies of commerce and industry (supervising organizations) accept technical intern trainees for technical intern training at affiliated enterprises (implementing organizations)
After technical intern trainees enter Japan, they undergo Japanese language lectures and other lectures to acquire knowledge and information necessary for their legal protection and then acquire practical Skills etc. under an employment relationship with a Japanese enterprise or other business (implementing organization) (in the case of the individual enterprise type training, the lecture implementation period need not begin immediately after entering the country).
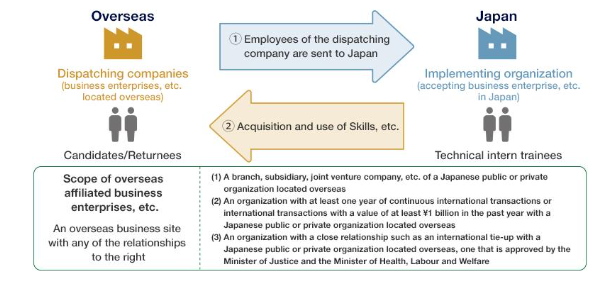
Individual Enterprise Type
A format whereby enterprises and other businesses in Japan (implementing organizations) accept employees of overseas local subsidiaries, joint venture companies, or trading partners and conduct technical intern training.
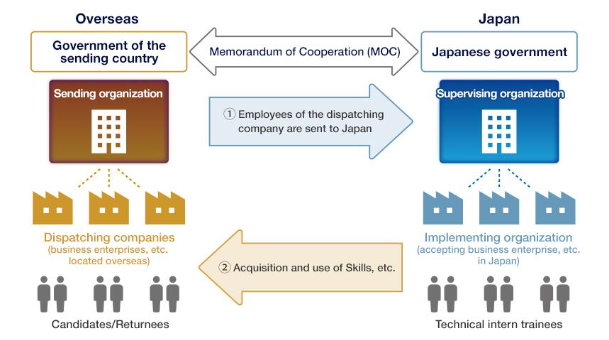
Supervising Organization Type Training
A format whereby non-profit organizations such as business cooperatives and societies of commerce and industry (supervising organizations) accept technical intern trainees for technical intern training at affiliated enterprises (implementing organizations)
3 Technical Intern Training Categories and Status of Residence
There are three technical intern training categories for both the individual enterprise type and supervising organization type trainee acceptance formats: activities for Skill etc. acquisition in the first year after entering Japan (Technical Intern Training (i)), activities to enhance Skills etc. in the second and third years after entering Japan (Technical Intern Training (ii)), and activities to master Skills etc. in the fourth and fifth years after entering Japan (Technical Intern Training (iii)).
Statuses of residence corresponding to the technical intern training categories are indicated in the following table.
| Individual Enterprise Type | Supervising Organization Type |
|---|---|---|
First year after entry | Individual Enterprise Type Technical Intern Training (i) | Supervising Organization Type Technical Intern Training (i) |
Second and third years after entry | Individual Enterprise Type Technical Intern Training (ii) | Supervising Organization Type Technical Intern Training (ii) |
Fourth and fifth years after entry | Individual Enterprise Type Technical Intern Training (iii) | Supervising Organization Type Technical Intern Training (iii) |
In order to make the shift from Technical Intern Training (i) to Technical Intern Training (ii), or from Technical Intern Training (ii) to Technical Intern Training (iii), the technical intern trainee must pass the specified Technical Intern Training Evaluation Examination (in the case of shift to Technical Intern Training (ii), a written test and practical test, and in the case of shift to Technical Intern Training (iii), a practical test).
The occupations and work eligible for transition to Technical Intern Training (ii) or Technical Intern Training (iii) (occupations and work subject to transfer) are specified by ordinances of the competent ministries.
Job categories Eligible When Interns Shift to Technical Intern Training (ii) (in Japanese only)
Organizations that can conduct Technical Intern Training (iii) are limited to excellent supervising organization and implementing organizations that are deemed to satisfy the standards specified by the competent ministries. Refer to pages 12 to 14 below for specifics of the standards.
New Technical Intern Training Program (in Japanese only)
4 Process from Technical Intern Trainee Entry into JAPAN until Return to Home Country
The main details of the process from technical intern trainee entry into Japan until return to the trainee’s home country under the new Technical Intern Training Act is shown in the figure below.
Process from Technical Intern Trainee Entry into Japan until Return to Home Country
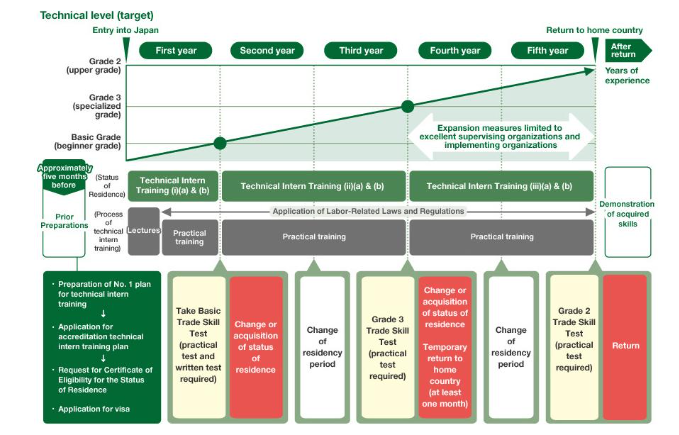
For technical intern trainees to be accepted under the supervising organization type program, the supervising organization must submit: an application for license of the supervising organization (the first time trainees are accepted), an application for accreditation of the technical intern training plan to the Organization for Technical Intern Training, and an application for a Certificate of Eligibility for the Status of Residence to the Immigration Bureau, in that order.
5Accreditation of Technical Intern Training Plan
A person that seeks to conduct technical intern training (an implementing organization) must prepare a technical intern training plan and receive accreditation of the suitability of the plan. Accreditation of technical intern training plan is performed by the Organization for Technical Intern Training.
Information that must be included in the technical intern training plan and documents that must be attached when submitting an application are specified in the Technical Intern Training Act and related laws.
The technical intern training plan must be accredited for grades 1, 2, and 3 for each technical training intern. Technical intern training plans for grade 3 in particular require that the implementing organization must “conform to the criteria provided for by an ordinance of the competent ministries as an entity with a high standard of capabilities to ensure the acquisition, etc. of the Skills etc.”
In the case of supervising organization type training, the implementing organization prepares a technical intern training plan and must receive guidance from the supervising organization that supervises the training.
The implementing organization must conduct the technical intern training in accordance with the accredited technical intern training plan. If a violation occurs, the organization will be subject to an order for improvement or cancellation of accreditation.
JITCO provides support services to implementing and supervising organizations with regard to the procedures for applying for accreditation of technical intern training plans and subsequent necessary entry and residence applications.
Japan – A Favourable Destination for Skilled People
Japan, the world’s third-largest economy, has been increasingly experiencing the issue of population aging. More than 20% of Japan’s population is over 65 years, the world’s highest proportion. As per a report by McKinsey, Japan’s working-age population will decline to 71 million in 2025 from 79 million in 2012, and its dependency ratio is set to soar from 0.60 to 0.73 over the same period. There are not enough young people in Japan to fill this vacuum due to the decline in its fertility rate. Given the nation’s aging issue and shrinking population, labor shortage needs to be addressed urgently. Thus, the Government of Japan has taken up certain measures such as premiums for employment of older workers, raising the mandatory retirement age, among others. Technical Intern Training Program (TITP) is one such program in Japan that promotes the acceptance of foreign human resources, who acquire skills and knowledge by working as technical interns in Japan.
“The best way to predict the future is to create it.” – Abraham Lincoln

